Rainwater harvesting is a great strategy for reducing domestic water use and protecting our homes and the land surrounding it. Harvesting rainwater can lead us to dozens of other practices that bring us into greater sustainability.
Design landscapes to manage and store rainwater:
最容易收集的雨水来源是落在院子里的雨水。适当地放置植物、树木和水源可以使场地成为一个高效的雨水管理系统。一些技术包括:用沼泽和护堤塑造土壤表面以减缓径流,抬高路径和天井,以及下沉所有种植区域以引导和收集水分。
Choose plants - primarily natives ones - that can absorb and hold water in their root systems or pass it down to the water table. This way, rainwater doesn’t run off into the street where it can collect toxic debris and chemicals, carrying them into local waterways.
Harvesting runoff:
The second source of rainwater is the street. Streets aren’t flat; they are typically graded so that water flows to the curb, down the block to a gutter and into the storm drain. In some cities, storm drains are connected to the sewage treatment plant and heavy rains can cause them to overflow, sending raw and partially treated sewage into lakes and rivers.
Other cities connect storm drains to underground creeks, and polluted water can run straight into nearby waterways and aquifers. If there are ways to divert water-to-water storage areas, you can change street rainwater from being a problem to a resource.
The third source of rainwater is the roof. Even in areas with low rainfall there is enormous potential for harvesting rainwater. A 1,000 square foot house can collect about 2,300 litres per inch of rain. So in an average year with 23 inches of rain in Toronto, for example, that small roof could collect 53,000 litres of water.
Rainwater collection and storage:
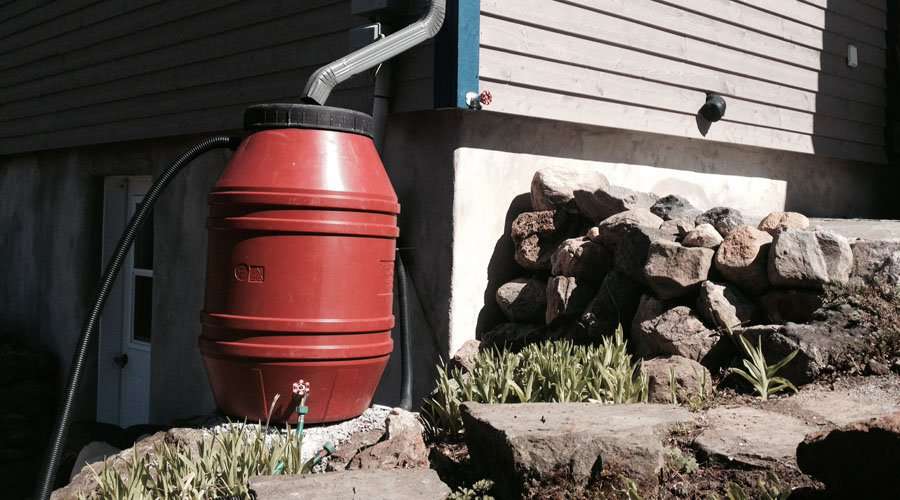
A water catchment system for roof rainwater is simple, and can store water for outdoor irrigation.
-
Gutters:Rainwater gathers in gutters, is directed to the downspout, or a 'first flush' pipe, then stored in barrels or cisterns. Rainwater harvesting 'first flush' clean out © Michael Casey
Rainwater harvesting 'first flush' clean out © Michael Casey - “First Flush”: The first rain of the year is the dirtiest as it cleans the roof. Water can be directed away from the tank in a first flush system (shown to the right) and subsequent water continues to the tank.
- Screen: tops of tanks should include screens to further filter leaves and debris and protect mosquitoes from breeding.
- Storage:地面上的水箱应该是深色的,以抑制藻类生长。它们还应该设计成在冬季安全运行,或者容易在季节安装和拆卸。
- Irrigation:A hose attachment is located near the bottom for irrigation.
- Overflow:Commercially available rain barrels should should come with an overflow tube or at least a whole where one can be installed. This enables connecting multiple barrels together for additional storage to ensure you can capture as much as you wish (see image below right).
 |
|
Multipe rain barrel system © Ecohome
|
Rain barrels are a popular way to begin rainwater harvesting, especially in urban areas. They are low cost and can be installed beside houses, under decks, or in other unused spaces.
There is a huge range of options for large single storage tanks (cisterns). They can be made from plastic, ferrocement, metal or fiberglass, and range in size from 50 gallons to thousands of gallons.
Indoor use:
Stored rainwater can be very safely used for toilet flushing and showers. EPA and other research has shown that rainwater harvested using a "first flush" system and protected from light is safe to use for bathing and other household use.
 |
|
|
有一个相当大的地下蓄水池,它可以满足一个家庭全年的冲洗需求,只需要雨水,因为系统可以在冬天用融雪在温暖的日子充电。
Drinking rainwater:
使用被动过滤器(如右图所示的陶瓷过滤器)或慢砂过滤器只过滤少量用于饮用的水,大大降低了系统成本,并为需要清洁饮用水的人们提供了一种负担得起的解决方案。
























我喜欢这篇文章和想法,但是....我认为一年的水的数学是不对的这里是谷歌说....https://www.google.com/sear...
That was definitely a funky number, thanks for catching that!
Rainwater harvesting is the method of collecting rainwater from an impervious surface and directing it to a location where it shall be used or stored for later utilize. The process wherein it is stored in tanks for residential or commercial use is active rainwater harvesting.